Regional Council of Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
The Regional Council of Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes (French: Conseil régional d'Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes) is the deliberative assembly of the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region in southeast-central France. The Regional Council of Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes succeeded the Regional Council of Auvergne and Regional Council of Rhône-Alpes.
Regional Council of Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes Conseil régional d'Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes | |
|---|---|
 Coat of arms of Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes | |
Logo of Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| History | |
| Preceded by | Regional Council of Auvergne Regional Council of Rhône-Alpes |
New session started | 2 July 2021 |
| Leadership | |
President | Fabrice Pannekoucke, LR since 5 September 2024 |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 204 |
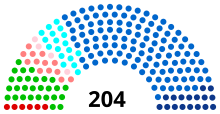 | |
Political groups | Majority (153)
Opposition (51) |
| Elections | |
| Two-round list proportional representation system with majority bonus | |
Last election | 20 and 27 June 2021 |
Next election | 2028 French regional elections |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| 1 Esplanade François Mitterrand CS 20033 – 69269 Lyon cedex 02 | |
 | |
| 59 Boulevard Léon Jouhaux CS 90706 – 63050 Clermont-Ferrand cedex 2 | |
| Website | |
| www | |
History
editThe Regional Council of Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes was created by the act on the delimitation of regions, regional and departmental elections and amending the electoral calendar of 16 January 2015, which went into effect on 1 January 2016 and merged the Regional Council of Auvergne and Regional Council of Rhône-Alpes,[1] consisting of 47 and 156 regional councillors, respectively, into a single body with 204 regional councillors, following regional elections on 6 and 13 December 2015.[2][3]
Seat
editAs Lyon was designated as the capital of the new region,[4] the official meeting place of the regional council of Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes is at the Hôtel de Région located in the district of La Confluence in the 2nd arrondissement of Lyon at 1 esplanade François Mitterrand.[5][6] Originally built at a cost of €147.1 million as the seat of the regional council of Rhône-Alpes, the construction of the building was approved by the regional council on 7 April 2005, followed by a European-level architecture competition from November 2005 to September 2006, the procurement of a building permit on 30 August 2007, groundbreaking on 8 July 2008, and the relocation of employees over a six-week period starting on 19 May 2011.[7]
On 21 June 2014, the new headquarters of the regional council of Auvergne at the Hôtel de Région in Clermont-Ferrand at 59 boulevard Léon Jouhaux was officially opened, built at a cost of €81 million. The fate of the project,[6][8] approved in 2007 with unanimous support,[9] was questioned given the selection of Lyon as the capital of the new region. Although Jean-Jack Queyranne, president of the regional council of Rhône-Alpes, suggested that the merged region could alternate between the two seats, with plenary assemblies in Lyon and standing committees in Clermont-Ferrand, the idea was scrapped given the comparison to the experience of the European Parliament with its two seats in Brussels and Strasbourg.[5] With Laurent Wauquiez, promising reduced costs, elected president of the region following the 2015 regional elections, any arrangement involving frequent travel between the two cities was definitively ruled out.[5] The building continues to house administrative functionaries,[10] with space rented out for associations and start-ups and serving as a venue for events and conferences in an effort to make the structure profitable.[11] The standing committee of the regional council also occasionally meets in Clermont-Ferrand.[12][13]
Election results
edit2015 regional election
editThe current regional council was elected in regional elections on 6 and 13 December 2015, with the list of Laurent Wauquiez consisting of The Republicans (LR), the Democratic Movement (MoDem), and the Union of Democrats and Independents (UDI) securing an absolute majority of 113 seats.[14][15]
| Leader | List | First round | Second round | Seats | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | Votes | % | Seats | % | |||
| Laurent Wauquiez | LR–MoDem–UDI | 795,661 | 31.73 | 1,201,597 | 40.62 | 113 | 55.39 | |
| Christophe Boudot | FN | 639,923 | 25.52 | 667,102 | 22.55 | 34 | 16.67 | |
| Jean-Jack Queyranne | PS–PRG | 600,112 | 23.93 | 1,089,756 | 36.84 | 57 | 27.94 | |
| Jean-Charles Kohlhaas | EELV–PG–ND | 173,038 | 6.90 | |||||
| Cécile Cukierman | PCF | 135,274 | 5.39 | |||||
| Gerbert Rambaud | DLF | 71,538 | 2.85 | |||||
| Éric Lafond | NC | 39,187 | 1.56 | |||||
| Chantal Gomez | LO | 31,359 | 1.25 | |||||
| Alain Fédèle | UPR | 21,723 | 0.87 | |||||
| Total | 2,507,815 | 100.00 | 2,958,455 | 100.00 | 204 | 100.00 | ||
| Valid votes | 2,507,815 | 96.55 | 2,958,455 | 96.58 | ||||
| Blank votes | 59,333 | 2.28 | 59,166 | 1.93 | ||||
| Null votes | 30,175 | 1.16 | 45,577 | 1.49 | ||||
| Turnout | 2,597,323 | 48.91 | 3,063,198 | 57.68 | ||||
| Abstentions | 2,713,316 | 51.09 | 2,247,266 | 42.32 | ||||
| Registered voters | 5,310,639 | 5,310,464 | ||||||
| Source: Ministry of the Interior, Le Monde (parties), Le Dauphiné Libéré (merged lists) | ||||||||
Composition
editPolitical groups
editThe regional council of Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes currently consists of seven political groups.
| Political group | Members | Parties | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LR–DVD–SC | The Republicans, Miscellaneous Right and Civil Society | 118 | LR, DVD | |
| LE | The Ecologists | 28 | EELV | |
| LD | The Democrats | 18 | UDI, MoDem | |
| RN | National Rally | 17 | RN | |
| SED | Socialists, Ecologists, Democrats | 13 | PS, DVG | |
| LFI-PCF | Insoumis and Communists | 6 | PCF, FI | |
| PRG | PRG | 4 | PRG | |
Executive
editPresidents
editLaurent Wauquiez was elected president of the regional council of Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes at its opening session in Lyon on 4 January 2016.[16]
| Candidate | Party | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laurent Wauquiez | LR | 113 | 55.39 | |
| Jean-François Debat | PS | 42 | 20.59 | |
| Christophe Boudot | FN | 34 | 16.67 | |
| Jean-Charles Kohlhaas | EELV | 8 | 3.92 | |
| Cécile Cukierman | PCF | 7 | 3.43 | |
| Votes | 204 | 100.00 | ||
| Blank and null votes | 0 | 0.00 | ||
| Valid votes | 204 | 100.00 | ||
Vice presidents
editIn addition to the president, the executive consists of 15 vice presidents and 14 advisers.[17][18]
| Number | Regional councillor | Group | Delegate for | Department | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st vice president | Etienne Blanc | LR–DVD–SC | Finance, general administration, budgetary savings and cross-border policies | Ain | |
| 2nd vice president | Brice Hortefeux | LR–DVD–SC | Territorial planning and solidarity with the Auvergnat territories | Puy-de-Dôme | |
| 3rd vice president | Béatrice Berthoux | LR–DVD–SC | Lycées | Rhône | |
| 4th vice president | Eric Fournier | LD | Environment, sustainable development, energy and regional nature parks | Haute-Savoie | |
| 5th vice president | Philippe Meunier | LR–DVD–SC | Security, international partnerships, hunting and fishing, airports and airport areas, forests and woodlands | Lyon Metropolis | |
| 6th vice president | Annabel André-Laurent | LR–DVD–SC | Enterprises, employment, economic development, trade, crafts and liberal professions | Haute-Savoie | |
| 7th vice president | Martine Guibert | LD | Transport | Cantal | |
| 8th vice president | Jean-Pierre Taite | LR–DVD–SC | Agriculture, viticulture and local produce | Loire | |
| 9th vice president | Samy Kefi-Jérôme | LR–DVD–SC | Social and family policies | Loire | |
| 10th vice president | Yannick Neuder | LR–DVD–SC | Higher education, research and innovation, health and European funds | Isère | |
| 11th vice president | Stéphanie Pernod-Beaudon | LR–DVD–SC | Vocational training and apprenticeship | Ain | |
| 12th vice president | Juliette Jarry | LR–DVD–SC | Infrastructure, economy and digital usages | Lyon Metropolis | |
| 13th vice president | Nicolas Daragon | LR–DVD–SC | Tourism and spa industry | Drôme | |
| 14th vice president | Florence Verney-Carron | LR–DVD–SC | Culture and heritage | Lyon Metropolis | |
| 15th vice president | Marie-Camille Rey | LR–DVD–SC | Youth, sport and associative life | Loire | |
Committees
editThe regional council includes 18 thematic committees with advisory roles, each composed of 38 members with a chairperson and two vice chairpersons. The comments of the thematic committees are considered by and submitted to a final vote of the standing committee or in a plenary session.[17][19] The standing committee consists of the president, 15 vice presidents, and 45 members of the regional council.[20]
| Committee | President | Group | Department | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Social action, city policy and housing | Jérôme Moroge | LR–DVD–SC | Lyon Metropolis | |
| Cultural affairs | Marlène Mourier | LR–DVD–SC | Drôme | |
| Agriculture, rurality, viticulture and food | Jean-Pierre Vigier | LR–DVD–SC | Haute-Loire | |
| Local economy, trade, crafts and liberal professions | Alain Berlioz-Curlet | LR–DVD–SC | Lyon Metropolis | |
| Higher education and research | Pierre Bérat | LR–DVD–SC | Lyon Metropolis | |
| Enterprise, economy and employment | Daniel Dugléry | LR–DVD–SC | Allier | |
| Environment, sustainable development and energy | Michèle Cedrin | LD | Isère | |
| Finance, general administration | Thierry Kovacs | LR–DVD–SC | Isère | |
| Continuing education and apprenticeship | Lionel Filippi | LD | Isère | |
| Initial education and lycées | Claude Aurias | LD | Drôme | |
| Mountain | Gilles Chabert | LR–DVD–SC | Isère | |
| Digital | Samy Kefi-Jerome | LD | Loire | |
| International relations and agricultural agreements | Alain Marleix | LR–DVD–SC | Cantal | |
| Health, family, and disabled persons policy | Isabelle Masseboeuf | LD | Ardèche | |
| Security | Yves-Marie Uhlrich | LD | Lyon Metropolis | |
| Tourism and spa industry | Annabel André-Laurent | LR–DVD–SC | Haute-Savoie | |
| Transport, territorial planning and infrastructure | Jean-Pierre Taite | LR–DVD–SC | Loire | |
| Associative life, sport and youth | Xavier Breton | LR–DVD–SC | Ain | |
References
edit- ^ "Loi du 16 janvier 2015 relative à la délimitation des régions, aux élections régionales et départementales et modifiant le calendrier électoral". vie-publique.fr. 19 January 2015. Archived from the original on 13 July 2017. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ Céline Pauilhac (24 July 2014). "Malgré la fusion, Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes conserverait le même nombre de conseillers régionaux". France 3 Auvergne. Archived from the original on 29 January 2018. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ "Elections régionales 2015". vie-publique.fr. 23 November 2015. Archived from the original on 29 June 2017. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ Justin Boche (31 July 2015). "Lyon officiellement capitale de la région Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes". Lyon Capitale. Archived from the original on 29 January 2018. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ a b c Georges Bourquard (28 January 2016). "À saisir, "Région loue hémicycle…"". Le Dauphiné Libéré. Archived from the original on 29 January 2018. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ a b "Nous trouver". La Région Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes. Archived from the original on 29 January 2018. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ "La région Rhône-Alpes investit son nouveau siège lyonnais". Le Moniteur. 25 May 2011. Archived from the original on 29 January 2018. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ Evelyne Rimbert (21 June 2014). "Le nouvel Hôtel de la Région Auvergne officiellement inauguré sur fond de polémiques". France 3 Auvergne. Archived from the original on 29 January 2018. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ Jean-Paul Gondeau (24 April 2013). "Auvergne : polémique sur le coût du futur hôtel de Région". La Montagne. Archived from the original on 29 January 2018. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ Mathilde Siraud (14 January 2016). "Nouvelles régions : le casse-tête de la réorganisation administrative". Le Figaro. Archived from the original on 29 January 2018. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ Anne-Laure Dagnet (10 January 2016). "A louer : hôtel de région à Clermont-Ferrand pour cause de fusion". franceinfo. Archived from the original on 29 January 2018. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ Mathilde Montagnon (25 May 2016). "Saint-Étienne : la culture, victime des dissensions entre Laurent Wauquiez et Gaël Perdriau ?". France Bleu Saint-Étienne Loire. Archived from the original on 29 January 2018. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ "Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes : l'opposition attaque la "clause Molière" en justice". Europe 1. Agence France-Presse. 27 March 2017. Archived from the original on 11 October 2017. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ "Résultats des élections régionales 2015". Ministère de l'Intérieur. 13 December 2015. Archived from the original on 6 September 2017. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ Pierre Breteau; Samuel Laurent; Maxime Vaudano (5 August 2015). "Elections régionales : quel est le candidat dans votre (nouvelle) région ?". Le Monde. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ "Les présidents des nouvelles régions françaises prennent les commandes". L'Express. Agence France-Presse. 4 January 2016. Archived from the original on 29 January 2018. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ a b "Les élus". La Région Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes. Archived from the original on 29 January 2018. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ "Le Président et l'exécutif". La Région Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes. Archived from the original on 20 February 2018. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ "Les délibérations de l'assemblée régionale". La Région Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes. Archived from the original on 29 January 2018. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ^ Stéphane Moccozet (4 January 2016). "Conseil Régional d'Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes : qui sont les vice-présidents ?". France 3 Auvergne. Archived from the original on 29 January 2018. Retrieved 28 January 2018.