The Oriental turtle dove or rufous turtle dove (Streptopelia orientalis) is a member of the bird family Columbidae. The species has a wide native distribution range from Central Asia east across Asia to Japan. The populations show variations in the patterning of plumage and have been designated into at least six named subspecies. Populations in the higher latitudes tend to migrate south in winter, while those closer to the tropics are sedentary. Vagrants have been recorded in North America. The species is predominantly granivorous and forages on the ground.
| Oriental turtle dove | |
|---|---|

| |
| S. o. erythrocephala from southern India with no grey on forehead | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Columbiformes |
| Family: | Columbidae |
| Genus: | Streptopelia |
| Species: | S. orientalis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Streptopelia orientalis (Latham, 1790)
| |
| |
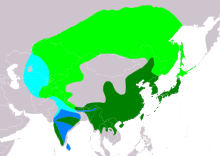
| Range of S. orientalis Breeding Resident Passage Non-breeding
| |
Taxonomy
edit| Relationship with congeneric species. Maximum likelihood phylogeny based on a 2001 study.[2] |
The genus name Streptopelia is from Ancient Greek streptos, "collar" and peleia, "dove". The specific orientalis is Latin for "eastern", in this case referring to the type locality, China.[3]
The species has a wide distribution with geographical variation in plumage that has led to at least six subspecies being designated. The distributions of many are not disjunct and gradation exists except in some island populations. Some of the populations of Streptopelia turtur that occur on the eastern edge can be very similar in appearance to S. orientalis and in the past the two species have been lumped together.[4][5]
- western Oriental turtle dove (S. o. meena) (Sykes, 1832) – eastern Asia and Central Asia south to the Himalayas from Kashmir to central Nepal. Winters in India as far south as Sri Lanka.
- eastern Oriental turtle dove (S. o. orientalis) (Latham, 1790) – central Siberia to Japan and Korea south to the Himalayas from Assam to Yunnan and northern Vietnam. Winters in South and Southeast Asia (includes S. baicalensis Buturlin).
- S. o. stimpsoni (Stejneger, 1887) – the Ryukyu Islands
- S. o. orii Yamashina, 1932 – Taiwan
- S. o. erythrocephala (Bonaparte, 1855) – southern peninsular India. This subspecies is reddish-brown on the head with no grey on the forehead or crown, unlike the other subspecies. The undertail coverts and terminal tail band are slaty grey.[6]
- S. o. agricola (Tickell, 1833) – from Orissa and Bengal to northeastern India and into Myanmar south to Hainan
The Oriental turtle dove has two distinct migratory northern subspecies, S. o. orientalis in the central Siberian taiga, and S. o. meena in the open woodlands of Central Asia. The differences in the tail patterns of the subspecies S. o. orientalis and S. o. meena help separate identification in their wintering grounds. The nominate form is described as having a grey tip to the tail and more black in the outer web of the outer tail feathers, while meena has a white tip to its tail like the European turtle dove and less black in the outer web of the outer tail feathers. However, these are not consistent differences: both forms can have white or grey tail-bands and orientalis can have little black in the outer webs of the outer tail feathers.[7]
Description
editThe Oriental dove is very similar in plumage to the Turtle dove. It is a little larger than that species, particularly in the case of orientalis, about the same size as a collared dove. It shares the black and white striped patch on the side of its neck made of silver-tipped feathers, but the breast is less pink, and the orange-brown wing feathers of the turtle dove are replaced with a browner hue, and darker centres giving a scaly appearance. The tail is wedge shaped, like the turtle dove. The flight is more relaxed and direct than that of its relative. Additionally, the turtle-dove has a bare patch of skin around its eyes, which the oriental dove lacks.[8]
Call
editThe calls are different from the purring of the European turtle dove. It is a four-syllable her-her-oo-oo. There are significant call differences within the populations as well.[9]
Distribution and habitat
editThe habitat varies, but the Oriental turtle dove breeds in well-wooded but open habitats and winters in more open habitats but usually with good tree cover.[9]
The westernmost race, meena, breeds in the Western Palearctic region.[10] The southernmost populations are resident, but most other birds migrate south to winter in India, the Maldives, and southern Japan. They disperse widely and are known from islands such as the Lakshadweep in winter.[9] S. o. orientalis occurs as a rarity in western Alaska and British Columbia. It is also a vagrant to northern and western Europe and occurrences in Britain tend to gather much attention from twitchers.[11]
Ecology
editBreeding
editThe summer breeding season in the temperate zone can be protracted. In southern India, the breeding season is in winter. In display, the male flaps its wing noisily and shoots up before gliding down with outspread tail.[12] Nests take about two days to build with the male gathering material and the female placing it. The nest is more substantial than in some other doves and is placed at mid-canopy height. In Japan, nests built at a greater height tended to be prone to predation.[13] Males were found to incubate in the day and the female by night. Two white eggs, as for all pigeons and doves, are laid in a twig nest in a tree. Incubation begins immediately after the first egg is laid. The eggs hatch in 15 to 16 days and the chicks take about 15 to 17 days to fledge (in Japan). Both parents feed the altricial chicks with crop milk. Multiple broods may be raised and nests built by the pair or by others may be reused. Nest reuse may possibly increase the chances of predation.[14][15] In Japan the principal predators of nestlings and eggs were crows and magpies and to a lesser extent cats and snakes.[16]
Diet
editThe Oriental turtle dove is granivorous, and feeds on the seeds of hemp, sunflower, wheat, millet and amaranth. It also consumes gastropods.[10] They forage on the ground.[17]
Parasites and diseases
editNests in Japan that have accumulated faeces have been found to host a number of flies belonging to the families Sphaeroceridae, Sepsidae, and Stratiomyidae.[18]
Subcutaneous mites of the species Hypodectes propus have been recorded in Japan.[19] Deaths of a number of birds due to avian pox virus have been recorded in South Korea.[20]
Other associations
editOn Hongdo Island, Korea, migratory doves were found to carry seeds of the exotic Achyranthes japonica attached to their plumage.[21]
In culture
editThe Ainu people traditionally interpret bird calls as elaborate sayings in their own language. In the case of these doves, the ascribed saying, an amalgam of several, is as follows:
Kusuwep toyta |
Turtle dove ploughs, |
The reason the dove is said to be 'ploughing' is that it is often seen burrowing in the fields with its feet in search of food, and thus appears as such.[22]
Gallery
edit-
Oriental turtle dove
-
Oriental turtle doves forage on the ground for their food
-
In Nepal
-
In Nepal
-
In Uttrakhand, India
-
In Hsinchu City, Taiwan
-
In Hsinchu City, Taiwan
References
edit- ^ BirdLife International (2016). "Streptopelia orientalis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22690439A93273750. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22690439A93273750.en. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- ^ Johnson, Kevin P; De Kort, Selvino; Dinwoodey, Karen; Mateman, A. C; Ten Cate, Carel; Lessells, C. M; Clayton, Dale H (2001). "A Molecular Phylogeny of the Dove Genera Streptopelia and Columba" (PDF). The Auk. 118 (4): 874. doi:10.1642/0004-8038(2001)118[0874:AMPOTD]2.0.CO;2. hdl:20.500.11755/a92515bb-c1c6-4c0e-ae9a-849936c41ca2.
- ^ Jobling, James A (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. pp. 284, 367. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
- ^ Baker, E.C. Stuart (1913). Indian Pigeons and Doves. London: Witherby and Co. pp. 185–201.
- ^ Peters, James Lee (1937). Check-list of birds of the World. Volume III. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. pp. 88–90.
- ^ Ali, Salim; Ripley, S. Dillon (1981). Handbook of the Birds of India and Pakistan. Volume 3. Stone curlews to owls (2 ed.). Delhi: Oxford University Press. pp. 142–146.
- ^ Leader, Paul J. (2004) Tail pattern of Oriental Turtle Dove British Birds 97(2): 98–100
- ^ "Birds of northern xinjiang". Shanghaibirding. Retrieved 7 September 2022.
- ^ a b c Rasmussen, P.C.; Anderton, J.C. (2005). Birds of South Asia. The Ripley Guide. Volume 2: Attributes and Status. Lynx Edicions and Smithsonian Institution. p. 208.
- ^ a b Wilson, Michael G.; Korovin, Vadim A. (2003). "Oriental Turtle Dove breeding in the Western Palearctic". British Birds. 96 (5): 234–241.
- ^ Hirschfeld, Erik (1986). "Rufous Turtle Dove in Europe". Dutch Birding. 8 (3): 77–84.
- ^ Singh, K. Shamungou (1998). "Aerial display of rufous turtle dove Streptopelia orientalis agricola Tickell near Nambol Bazar, Manipur". Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society. 95: 114.
- ^ Wada, Takeshi (1994). "Effects of Height of Neighboring Nests on Nest Predation in the Rufous Turtle-Dove (Streptopelia orientalis)" (PDF). The Condor. 96 (3): 812–816. doi:10.2307/1369488. JSTOR 1369488.
- ^ Wada, Takeshi (1992). "An Implicit Cost of Nest Re-use in the Rufous Turtle Dove Streptopelia orientalis". Jap. J. Ornithol. 40 (2): 43–50. doi:10.3838/jjo.40.43.
- ^ Haneda, Kenzo; Nozawa, Shinosuke (1969). "A study on the life history of Streptopelia orientalis". Journal of the Yamashina Institute for Ornithology. 5 (5): 473–486. doi:10.3312/jyio1952.5.5_473. ISSN 0044-0183.
- ^ Kameda, Kayoko (1994). "Identification of nest predators of the rufous turtle dove Streptopelia orientalis by video tape recording". Jap. J. Ornithol. 43: 29–31. doi:10.3838/jjo.43.29.
- ^ Ali, S; Ripley, SD (1981). Handbook of the birds of India and Pakistan. Volume 3 (2 ed.). Oxford University Press. pp. 142–147.
- ^ Iwasa, Mitsuhiro; Hori, Koji; Aoki, Noriyuki (1995). "Fly fauna of bird nests in Hokkaido, Japan (Diptera)". The Canadian Entomologist. 127 (5): 613–621. doi:10.4039/Ent127613-5. ISSN 1918-3240.
- ^ El-Dakhly, Khaled Mohamed; El-Nahass, El-Shaymaa; Inui, Kosei; Kimura, Junpei; Sakai, Hiroki; Yanai, Tokuma (2013-12-01). "Hypodectes propus(Acarina: Hypoderatidae) in a rufous turtle dove,Streptopelia orientalis(Aves: Columbiformes), in Japan". Journal of Veterinary Science. 14 (4): 421–4. doi:10.4142/jvs.2013.14.4.421. ISSN 1229-845X. PMC 3885735. PMID 23820220.
- ^ Lee, Hae Rim; Koo, Bon-Sang; Kim, Jong-Taek; Kim, Heung-Chul; Kim, Myung-Soon; Klein, Terry A.; Shin, Man-Seok; Lee, Sanghun; Jeon, Eun-Ok (2017-10-01). "Molecular epidemiology of avian poxvirus in the oriental turtle dove (Streptopelia orientalis) and the biting midge (Culicoides arakawae) in the Republic of Korea". Journal of Wildlife Diseases. 53 (4): 749–760. doi:10.7589/2016-10-230. ISSN 0090-3558. PMID 28700322. S2CID 4386661.
- ^ Choi, Chang-Yong; Nam, Hyun-Young; Chae, Hee-Young (2010). "Exotic Seeds on the Feathers of Migratory Birds on a Stopover Island in Korea". Journal of Ecology and Environment. 33 (1): 19–22. Bibcode:2010JEcEn..33...19C. doi:10.5141/jefb.2010.33.1.019.
- ^ Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Nakamoto, Mutsuko (2014). Kamuy Yukar wo Kiite Ainu-go wo Manabu カムイユカㇻを聞いてアイヌ語を学ぶ [Learn Ainu by Listening to Kamuy Yukar] (in Japanese). Tokyo: Hakusuisha. pp. 21, 23.
Notes
edit- ^ It is not clear who the “master” is here. Some say it is the ethnic Yamato exploiting the Ainu people, a position supported by the fact that the word for 'master' used here, tono, is a Japanese loanword. However, the Ainu people also refer to some animals by this title, such as isepo tono 'lord rabbit' or sisoya tono 'lord wasp'. It is also possible that this expression simply refers to the young child of the household.
Bibliography
edit- "National Geographic" Field Guide to the Birds of North America ISBN
- Handbook of the Birds of the World Vol 4, Josep del Hoyo editor, ISBN
