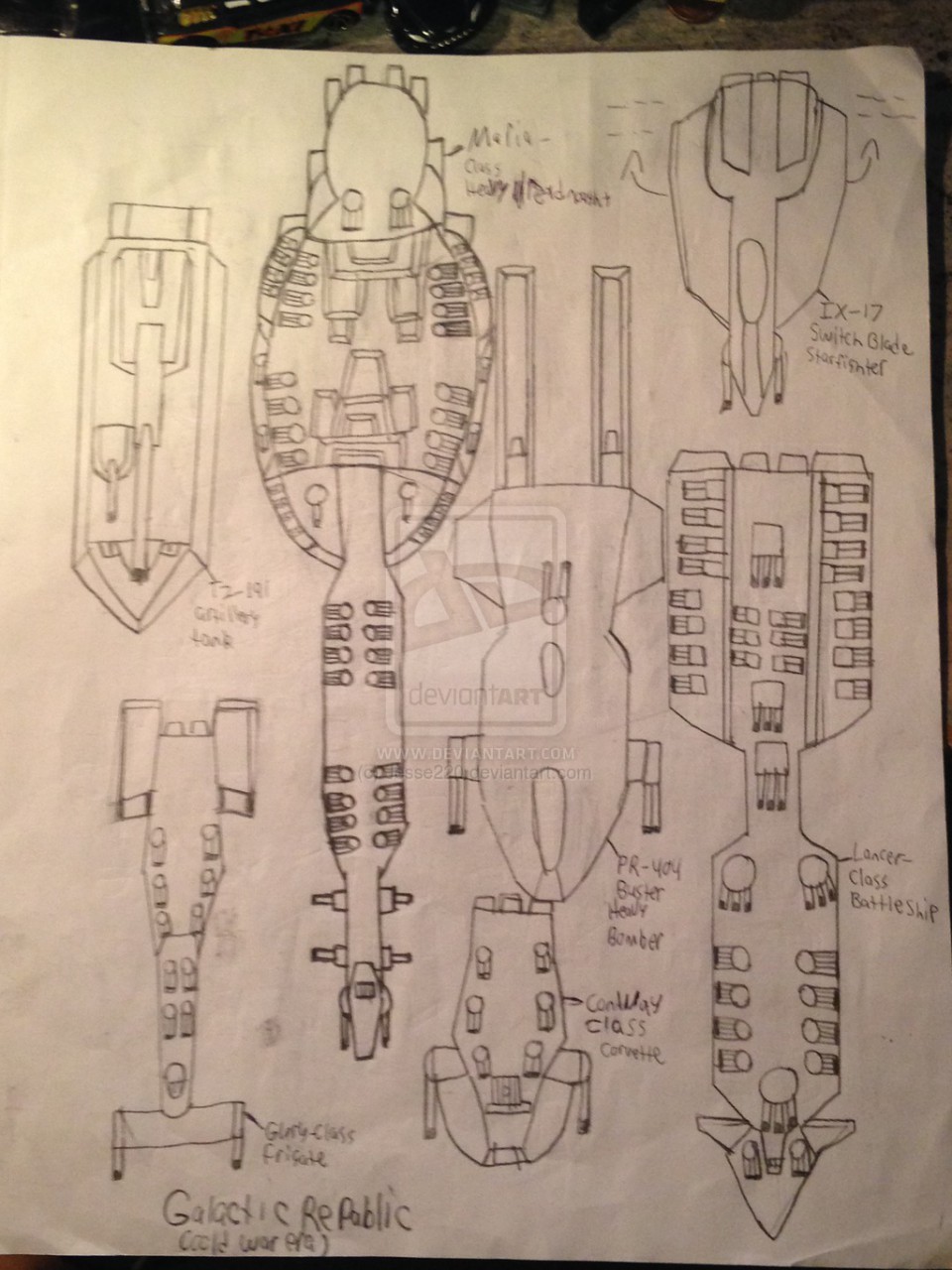
I made those ships and a tank for the Galactic Republic during the Great Galactic War. Here we have a Maria-Class Heavy Dreadnought, designed to handle any enemy fire power and was used for battles. Centuries later, The Maria- Class Heavy Dreadnought was reproduce and later used by the Rebel Alliance with upgraded technology and firepower. And we have a Lancer-Class Battleship also used by the republic during the war.
Category All / All
Species Unspecified / Any
Gender Any
Size 960 x 1280px
File Size 220 kB

 FA+
FA+



Comments