The chiasmatic groove (chiasmatic sulcus, optic groove, prechiasmatic sulcus) is a transverse[1] groove upon the superior aspect of the body of sphenoid bone[1][2]: 509 within the middle cranial fossa.[2]: 508-509 It is bounded anteriorly by the sphenoidal limbus (a variably prominent ridge also representing the posterior boundary of the sphenoidal jugum[3]), and posteriorly by the tuberculum sellae.[1] The opening of each optic canal is placed at either lateral end of the chiasmatic sulcus. The optic chiasm is situated superior and quite posterior to the chiasmatic groove (and not against the groove as the name suggests).[2]: 509
| Chiasmatic groove | |
|---|---|
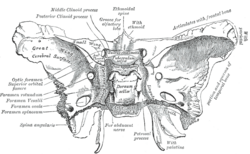 ethmoid bone. Upper surface. (Sulcus chiasmaticus labeled at center) | |
 Base of the skull. Upper surface. (Sphenoid bone is yellow; chiasmatic groove labeled at center left, fourth from the top of the labels near the yellow region.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | sulcus praechiasmaticus, sulcus chiasmaticus |
| TA98 | A02.1.05.005 |
| TA2 | 588 |
| FMA | 75760 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |

References
edit- ^ a b c "chiasmatic sulcus". TheFreeDictionary.com. Retrieved 2023-08-01.
- ^ a b c Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
- ^ "limbus sphenoidalis". TheFreeDictionary.com. Retrieved 2023-08-01.
External links
edit- figures/chapter_42/42-18.HTM: Basic Human Anatomy at Dartmouth Medical School
- Anatomy image: skel/internal2 at Human Anatomy Lecture (Biology 129), Pennsylvania State University (#7)