A dwarf star is a star of relatively small size and low luminosity. Most main sequence stars are dwarf stars. The meaning of the word "dwarf" was later extended to some star-sized objects that are not stars, and compact stellar remnants that are no longer stars.
History
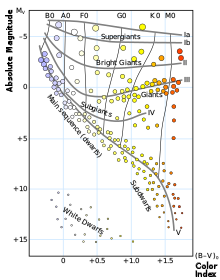
editThe term was originally coined in 1906 when the Danish astronomer Ejnar Hertzsprung noticed that the reddest stars – classified as K and M in the Harvard scheme – could be divided into two distinct groups. They are either much brighter than the Sun, or much fainter. To distinguish these groups, he called them "giant" and "dwarf" stars,[1] the dwarf stars being fainter and the giants being brighter than the Sun.
Most stars are currently classified under the Morgan Keenan System using the letters O, B, A, F, G, K, and M, a sequence from the hottest: type O, to the coolest: type M.
With the development of infrared astronomy in the late 20th century the Morgan Keenan system was extended to cooler types L and T, all of which are "dwarfs" but not all of which are stars as such.
Current uses of the term "dwarf"
editThe scope of the term "dwarf" at present includes the following:
- Dwarf star with no other qualification generally refers to a main-sequence star, a star of luminosity class V: main-sequence stars (dwarfs). Example: Achernar (B6Vep)[2]
- Red dwarfs are low-mass main-sequence stars.
- Yellow dwarfs are main-sequence (dwarf) stars with masses comparable to that of the Sun.
- Orange dwarfs are K-type main-sequence stars.
- Blue (type O and type B) main sequence stars are so large that they are difficult to distinguish from blue giant stars, either in size or brightness, and because of the cognitive dissonance, the word "dwarf" is avoided when referring to them.
- A blue dwarf is a hypothesized class of very-low-mass stars that increase in temperature as they near the end of their main-sequence lifetime. (It is believed that the universe is not old enough for any red dwarf to have yet reached the so-called "blue" stage, which is actually more of a medium white.
- A white dwarf is the remains of a dead star, composed of electron-degenerate matter. It is thought to be the final stage in the evolution of stars not massive enough to collapse into a neutron star or black hole – stars less massive than roughly 9 M☉.
- A black dwarf is theorized as a white dwarf that has cooled sufficiently that it no longer emits any visible light. It is believed that the universe is not old enough for any white dwarf to have yet cooled to "black".
- A brown dwarf is a substellar object not massive enough to ever fuse hydrogen into helium, but still massive enough to fuse deuterium – less than about 0.08 M☉ and more than about 13 Jupiter masses.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Brown, Laurie M.; Pais, Abraham; Pippard, A.B., eds. (1995). Twentieth Century Physics. Bristol, UK; New York, NY: Institute of Physics, American Institute of Physics. p. 1696. ISBN 0-7503-0310-7. OCLC 33102501.
- ^ Nazé, Y. (November 2009). "Hot stars observed by XMM-Newton. I. The catalog and the properties of OB stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 506 (2): 1055–1064. arXiv:0908.1461. Bibcode:2009A&A...506.1055N. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200912659. S2CID 17317459.[permanent dead link]