This article needs additional citations for verification. (June 2014) |
The Hackensack River is a river, approximately 45 miles (72 km) long, in the U.S. states of New York and New Jersey, emptying into Newark Bay, a back chamber of New York Harbor. The watershed of the river includes part of the suburban area outside New York City just west of the lower Hudson River, which it roughly parallels, separated from it by the New Jersey Palisades. It also flows through and drains the New Jersey Meadowlands. The lower river, which is navigable as far as the city of Hackensack,[1] is heavily industrialized and forms a commercial extension of Newark Bay.
| Hackensack River | |
|---|---|
 A view of the Hackensack River taken from the shore in Teaneck at low tide | |
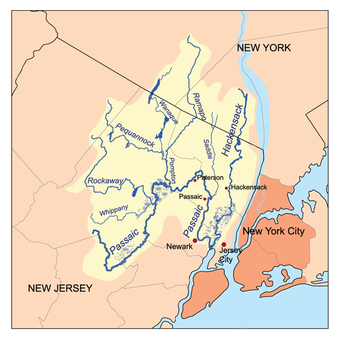 The Passaic and Hackensack watersheds | |
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| State | New Jersey, New York |
| Counties | Hudson, NJ, Bergen, NJ, Rockland, NY |
| City | Hackensack, NJ |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | New City, Rockland County, New York, United States |
| • coordinates | 41°11′00″N 73°59′24″W / 41.18333°N 73.99000°W |
| • elevation | 120 ft (37 m) |
| Mouth | Newark Bay |
• location | Hudson County, New Jersey, United States |
• coordinates | 40°42′55″N 74°06′42″W / 40.71528°N 74.11167°W |
• elevation | 0 ft (0 m) |
| Length | 54 mi (87 km) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | New Milford, NJ |
| • minimum | 0 cu ft/s (0 m3/s) |
| • maximum | 880 cu ft/s (25 m3/s) |
Once believed to be among the most polluted watercourses in the United States, it staged a modest revival by the late 2000s. The river is divided into the upper river, north of the Oradell Reservoir and Oradell Dam, and lower river, south of the reservoir and dam.
Description
editThe Hackensack River rises in southeastern New York, in Rockland County, in the Sweet Swamp, located in the hamlet of New City just west of the Hudson River and half a mile south of High Tor State Park. It flows briefly southeast, into the Lake DeForest reservoir, separated from the Hudson by less than 3 mi (5 km). South of the dam, it then flows south, diverging from the Hudson. Just across the New Jersey state line, in northern Bergen County, it is impounded to form the reservoir Lake Tappan near River Vale.
South of Lake Tappan, it flows in a meandering course southward through the suburban communities of New Jersey. Near Oradell, it is impounded to form Oradell Reservoir, where it is surrounded primarily by Oradell, Haworth, and Emerson, and joined by several streams, including the Dwars Kill, the Cherry Brook, and Pascack Brook. Van Buskirk Island, a man-made island and site of the New Milford Plant of the Hackensack Water Company, lies in this area. South of the reservoir, it flows through the Oradell Dam through River Edge, Hackensack, Teaneck, Bogota, and Ridgefield Park, once again approaching within 3 mi (5 km) of the Hudson, and separated from it by the ridge of the Palisades.
At Little Ferry, it is joined by the broad Overpeck Creek, then flows southward, widening in a broad meandering tidal estuary through the Meadowlands, forming extensive side streams and wetlands. South of North Bergen, it forms the boundary between Bergen County to the west and Hudson County to the east. Opposite Secaucus it is joined by Berry's Creek, then flows past the western edge of Jersey City, which overlooks the river's valley from the ridge of the Palisades, before forming Newark Bay at its confluence with the Passaic River between Jersey City and Kearny.
As it flows through the Meadowlands it is traversed by numerous rail and road bridges.
History
editThe name of the Hackensack River comes from the Lenape word Achinigeu-hach, or Ackingsah-sack, meaning flat confluence of streams [citation needed] or stony ground.[2] Conflicts with the Lenape prevented the early Dutch settlers of the New Netherland colony from expanding westward into the valley into late in the 17th century. The river furnished both the Native Americans and the European settlers with abundant runs of herring, shad and striped bass.
At the outset of the colonial era the river's watershed was home to Lenape groups now known as the Rumachenanck (or Haverstraw), Tappan, and Hackensack, the latter exonym taken from an encampment near the confluence of the tributary Overpeck Creek.[3] European settlement began in the mid 17th century as part of New Netherland when the region was called Achter Kol, meaning "rear pass" or "behind the ridge", to describe the valleys west of the Hudson Palisades which afforded passage to trapping grounds in the northern hinterlands.
The river and the surrounding Meadowlands presented a formidable difficulty in transportation and communication. The wetlands helped allow the escape of the Continental Army under George Washington in 1776 after several defeats at the hands of the British army on the east side of the Hudson. It later served as a protective barrier that allowed Washington's army to encamp in the nearby hills near Morristown.
Urbanization and pollution
editHuman alterations to land in the Hackensack meadowlands increased in the 19th century, including clearing forests; building roads, railroads and ditches; and filling wetlands.[4]: 34–36 The Second Industrial Revolution led to construction of heavy manufacturing, storage tanks, and chemical processing plants in the area during the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
The economic development and population increases in the watershed led to extensive water pollution in the river, both from municipal sewage and industrial wastewater. In the 20th century untreated sewage discharges from the various towns and cities began to contribute significant amount of pollutants to the river. The first sewage plant with secondary treatment technology did not open until the 1950s, and more treatment capacity was added in the region in the following decades.[5] Water quality studies in the late 1980s indicated that the river continued to be impaired with low oxygen levels and nutrient pollution.[4]: 144 In the 21st century many communities in the watershed continue to be drained by combined sewers, which discharge untreated sewage during large rainstorms.[4]: 117
Development of new drinking water supplies also had major environmental impacts on the river. The construction of the Oradell Reservoir dam in 1921 essentially changed the lower river from a free-flowing stream into a brackish estuary, allowing the encroachment of marine species.[4]: 112 Urbanization in the region intensified after World War II, with the expansion of roads and highways, including the New Jersey Turnpike (1952),[6] as well as the Meadowlands Sports Complex (1970s).[7]
By the 1960s, much of the lower river was essentially a turbid hypoxic dead zone, with only the hardiest of species, such as the mummichog, able to survive in its waters. Chemical companies dumped large volumes of waste into Berry's Creek during the 20th century, resulting in the highest concentrations of methyl mercury of any fresh-water sediment in the world, as well as extensive residues of PCBs and other chemicals.[8][9] Three sites along the creek are federally-designated Superfund sites and require major cleanup operations, which are ongoing as of 2022.[10][11][12]
The river recovered somewhat by the late 2000s following the decline in manufacturing in the area, as well as from enforcement of Clean Water Act regulations and from the efforts of local conservancy groups. Recreational fishing has staged a modest comeback, although catch and release may be advisable, as there are continuing health advisories against the consumption of fish caught in the river.[13] Urban runoff pollution, municipal sewage discharges from sanitary sewer overflows and combined sewer overflows, and runoff from hazardous waste sites continue to impair the river's water quality.[14][15]
The future of the wetlands around the lower river has been an ongoing controversy between development and preservation groups in recent decades. The Hackensack Meadowlands Development Commission, later called the New Jersey Meadowlands Commission, was established by the state in 1968 to manage development and habitat preservation.[16] The commission was merged into the New Jersey Sports and Exposition Authority in 2015.[17]
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) proposed designating the Lower Hackensack as a Superfund site, which would make it eligible for environmental remediation partially funded by original polluters.[18][19] In September 2022, the Lower Hackensack was declared a federal Superfund site, triggering the process.[20][21][22]
Tributaries
editNew Jersey
edit- Berry's Creek
- Bashes Creek
- Cherry Brook
- Moonachie Creek
- Mill Creek
- Cromakill Creek
- Bellmans Creek
- Losen Slote
- Overpeck Creek
- Coles Brook
- French Brook
- Hirshfeld Brook
- Dwars Kill
- Tappan Run
- Pascack Brook
- Holdrum Brook
- Hillsdale Brook
- Cherry Brook
New York
edit- Nauraushaun Brook Nanuet, New York
- East Branch Hackensack River
- Toms Creek
- West Branch Hackensack River
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ "117.723 Hackensack River", Title 33: Navigation and Navigable Waters Part 117—Drawbridge Operations Regulations, US Government Printing Office, October 20, 2012, retrieved 2012-10-20
- ^ "Bergen County Hist Society: Indigenous People of Bergen County". Archived from the original on 2019-01-20. Retrieved 2010-12-14.
- ^ Wright, Kevin. "The Indigenous Population of Bergen County". Bergen County Historical Society. Archived from the original on January 20, 2019. Retrieved November 1, 2012.
- ^ a b c d The Hackensack Meadowlands Initiative: Preliminary Conservation Planning for the Hackensack Meadowlands, Hudson and Bergen Counties, New Jersey (Report). Pleasantville, NJ: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS). March 2007.
- ^ "About Water Pollution Control". Little Ferry, NJ: Bergen County Utilities Authority. Retrieved 2021-02-19.
- ^ Schwab Jr., Armand (1952-01-20). "City Linked to Super-Highway; New York Motorists Have Choice of Five Entrances To Jersey Turnpike". The New York Times.
- ^ Cady, Steve (1976-08-29). "Jersey Complex Opens Trot Track Wednesday". The New York Times.
- ^ State Dept. of Envtl. Prot. v. Ventron Corp., 94 NJ 473 (Supreme Court of New Jersey 1983).
- ^ "Berry's Creek/Berry's Creek Canal". Meadowlands Environmental Site Investigation Compilation. U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, New York District. May 2004.
- ^ "Scientific Chemical Processing Superfund Site". Superfund. New York, NY: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). 2022-06-30.
- ^ "Universal Oil Products Superfund Site". Superfund. EPA. 2022-06-30.
- ^ "Ventron/Velsicol, Wood Ridge Borough, NJ: Cleanup Activities". Superfund. EPA. Retrieved 2019-01-14.
- ^ "Newark Bay Complex (including Newark Bay, tidal Hackensack River, Arthur Kill, Kill Van Kull and tidal tributaries)". Fish Smart Eat Smart NJ. Trenton, NJ: New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection (NJDEP). 2018.
- ^ Wright, Jim. "Hackensack River is getting cleaner."The Record. August 26, 2007. Archived 2016-03-03 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Watershed Management Area 5 Factsheet" (PDF). NJDEP. 2007-07-17. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-03-27.
- ^ New Jersey Meadowlands Commission, Lyndhurst, NJ. "Wetlands Sites in the Meadowlands." Archived 2011-07-21 at the Wayback Machine Accessed 2009-02-27.
- ^ Sullivan, S.P. (5 February 2015). "Christie signs controversial Meadowlands overhaul, but says bill will be revised". NJ Advance Media.
- ^ Zeitlinger, Ron; Maher, Jake (2022-03-17). "Lower Hackensack River to be added to list of EPA Superfund sites". The Jersey Journal. Secaucus, NJ: Advance Local Media LLC.
- ^ "EPA Proposes to Add Lower Hackensack River in Bergen and Hudson Counties, New Jersey to Superfund List". EPA. 2022-03-17. News Release.
- ^ "Restoring the Lower Hackensack River: Investigation and Cleanup under EPA's Superfund Program". nj.gov. NJDEP.
- ^ Zeitlinger, Ron; Maher, Jake (March 17, 2022). "Lower Hackensack River to be added to list of EPA Superfund sites". The Jersey Journal. Retrieved September 8, 2022.
- ^ "Hackensack River added to list of NJ Superfund sites, triggering a miles-long cleanup". The Record. 2022-09-07. Retrieved 2022-09-08.
External links
edit- Bergen SWAN - Watershed Protection Group
- Hackensack Riverkeeper - Environmental organization
- Hackensack River tides Archived 2009-01-08 at the Wayback Machine - Fairleigh Dickinson University
- Hackensack River bridges
- Wild New Jersey: Fishes of the Hackensack River
- Friends of the Hackensack River Greenway through Teaneck
- Meadowlands Environment Center - Environmental education facility
- Meadowlands Research and Restoration Institute
- New Jersey Naval Museum Home of the W.W. II Submarine USS Ling (SS-297)
- USS Ling Photos on board the Submarine USS Ling SS-297
- NOAA Chart 12337, Passaic and Hackensack Rivers
- U.S. Geological Survey: NJ stream gaging stations