This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
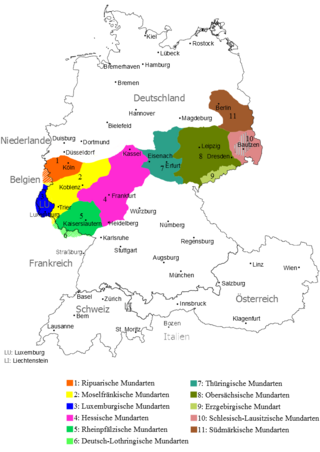
Ripuarian (/ˌrɪpjuˈɛəriən/ RIP-yoo-AIR-ee-ən) or Ripuarian Franconian[a] is a German dialect group, part of the West Central German language group. Together with the Moselle Franconian which includes the Luxembourgish language, Ripuarian belongs to the larger Central Franconian dialect family and also to the linguistic continuum with the Low Franconian languages.
| Ripuarian | |
|---|---|
| Native to | Germany, Belgium, Netherlands |
| Region | North Rhine-Westphalia, Rhineland-Palatinate, Liège Province, Limburg |
Native speakers | (Kölsch: 250,000 cited 1997)[1] |
Early forms | Proto-Indo-European
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | None (mis)Individual code: ksh – Kölsch |
| Glottolog | ripu1236 |
 Area where Ripuarian is spoken. Green = sparsely populated forest. | |
 Central German language area after 1945 and the expulsion of the Germans from the east. 1 = Ripuarian. | |
It is spoken in the Rhineland south of the Benrath line — from northwest of Düsseldorf and Cologne to Aachen in the west and to Waldbröl in the east.
The language area also comprises the north of the German-speaking Community of Belgium as well as the southern edge of the Limburg province of the Netherlands, especially Kerkrade (Kirchroa), where it is perceived as a variety of Limburgish and legally treated as such.[citation needed]
The name derives from the Ripuarian Franks (Rheinfranken), who settled in the area from the 4th century onward.
The most well known Ripuarian dialect is Kölsch, the local dialect of Cologne. Dialects belonging to the Ripuarian group almost always call themselves Platt (spelled plat in the Netherlands) like Öcher Platt (of Aachen), Bönnsch Platt (of Bonn), Eischwiele Platt (of Eschweiler), Kirchröadsj plat (of Kerkrade), or Bocheser plat (of Bocholtz). Most of the more than one hundred Ripuarian dialects are bound to one specific village or municipality. Usually there are small distinctive differences between neighbouring dialects (which are, however, easily noticeable to locals), and increasingly bigger differences between the more distant dialects. These are described by a set of isoglosses called the Rhenish fan in linguistics. The way people talk, even if they are not using Ripuarian, often allows them to be traced precisely to a village or city quarter where they learned to speak.
Number of speakers
editAbout a million people speak a variation of Ripuarian dialect, which constitutes about one quarter of the inhabitants of the area. Penetration of Ripuarian in everyday communication varies considerably, as does the percentage of Ripuarian speakers from one place to another. In some places there may only be a few elderly speakers left, while elsewhere Ripuarian usage is common in everyday life. Both in the genuine Ripuarian area and far around it, the number of people passively understanding Ripuarian to some extent exceeds the number of active speakers by far.
Geographic significance
editSpeakers are centred on the German city of Köln (Cologne). The language's distribution starts from the important geographic transition into the flat-lands coming down from the Middle Rhine. The Ripuarian varieties are related to the Moselle Franconian languages spoken in the southern Rhineland (Rhineland-Palatinate and Saarland) in Germany, to the Luxembourgish language in Luxembourg, and to the Low Franconian Limburgish language in the Dutch province of Limburg. Most of the historic roots of Ripuarian languages are in Middle German, but there were other influences too, such as Latin, Low German, Dutch, French and Southern Meuse-Rhenish (Limburgish). Several elements of grammar are unique to Ripuarian and do not exist in the other languages of Germany.[citation needed]
The French Community of Belgium as well as the Netherlands officially recognise some Ripuarian dialects as minority languages, and the European Union likewise follows.[citation needed]
Varieties
editVarieties are or include:[2]
- West Ripuarian (Westripuarisch), around Aachen and a small area in East Belgium and the Netherlands
- Central Ripuarian (Zentralripuarisch)
- City Colognian (Stadtkölnisch)
- Country Colognian (Landkölnisch)
Grammar
editNumerals
editThe transcription from Münch,[3] in which the grave accent (`) and macron (¯) represent, respectively, accent 1 and 2 in the Central/Low Franconian pitch accent.
| Cardinals | Ordinals | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ēn | dę ìəštə |
| 2 | tswęī | dę tswę̀itə |
| 3 | dreī | dę drę̀itə |
| 4 | fiəꝛ | dę fiətə |
| 5 | fønəf | dę fønəftə |
| 6 | zęks | dę zękstə |
| 7 | zevə | dę zevəntə |
| 8 | āx | dę āxtə |
| 9 | nøŋ̀ | dę nøŋ̄tə |
| 10 | tsèn | dę tsèntə |
| 11 | eləf | dę eləftə |
| 12 | tsweləf | dę tsweləftə |
| 13 | drøksēn | dę drøksēntə |
| 14 | fiətsēn | dę fiətsēntə |
| 15 | fuftsēn | dę fuftsēntə |
| 16 | zęksēn | dę zęksēntə |
| 17 | zevətsēn | dę zevetsēntə |
| 18 | āxtsēn | dę āxtsēntə |
| 19 | nøŋ̄sēn | dę nøŋ̄tsēntə |
| 20 | tswantsiχ | dę tswantsiχstə |
| 21 | enəntswantsiχ | |
| 22 | tswęiəntswantsiχ | |
| 23 | dreiəntswantsiχ | |
| 24 | fiəꝛentswantsiχ | |
| 25 | fønəvəntswantsiχ | |
| 26 | zękzəntswantsiχ | |
| 27 | zevənəntswantsiχ | |
| 28 | āxəntswantsiχ | |
| 29 | nøŋəntswantsiχ | |
| 30 | dresiχ | dę dresiχstə |
| 40 | fiətsiχ | dę fiətsiχstə |
| 50 | fuftsiχ | dę fuftsiχstə |
| 60 | zęksiχ | dę zęksiχstə |
| 70 | zevəntsiχ | dę zevətsiχstə |
| 80 | āxtsiχ | dę āxtsiχstə |
| 90 | nøŋ̄siχ | dę nøŋ̄tsiχstə |
| 100 | hondəꝛt | dę hondəꝛtstə |
| 200 | tsweīhondəꝛt | |
| 1000 | dùzənt | dę dùzəntstə |
Pronouns
editRipuarian (excluding City-Colognian) emphasised personal pronouns:[3]
| 1st person | 2nd person | 3rd person m. / f. / n. |
reflexive pronoun (of the 3rd person) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singular | ||||||
| Nom. | iχ | du | hę̄ | zeī | ət | |
| Gen. | – | – | – | – | – | |
| Dat. | mīꝛ | dīꝛ | em̀ | ìꝛ | em̀ | ziχ |
| Acc. | miχ | diχ | en | zeī | ət | ziχ |
| Plural | ||||||
| Nom. | mīꝛ | īꝛ | zē | |||
| Gen. | – | – | – | |||
| Dat. | os | yχ | eǹə | ziχ | ||
| Acc. | os | yχ | zē | ziχ | ||
See also
editNotes
edit- ^ German: Ripuarisch [ʁipuˈ(ʔ)aːʁɪʃ] , ripuarische Mundart, ripuarischer Dialekt, ripuarisch-fränkische Mundart or Ribuarisch; Dutch: ripuarisch [ripyˈʋaːris] or noordmiddelfrankisch.
References
edit- ^ Ripuarian at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)
Kölsch at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022) - ^ Jürgen Erich Schmidt, Robert Möller, Historisches Westdeutsch/Rheinisch (Moselfränkisch, Ripuarisch, Südniederfränkisch), sub-chapter Das Ripuarische; in: Sprache und Raum: Ein internationales Handbuch der Sprachvariation. Band 4: Deutsch. Herausgegeben von Joachim Herrgen, Jürgen Erich Schmidt. Unter Mitarbeit von Hanna Fischer und Birgitte Ganswindt, volume 30.4 of Handbücher zur Sprach- und Kommunikationswissenschaft (Handbooks of Linguistics and Communication Science / Manuels de linguistique et des sciences de communication) (HSK), Berlin/Boston, 2019, p. 529f.
- ^ a b Grammatik der ripuarisch-fränkischen Mundart von Ferdinand Münch. Bonn, 1904, p. 8ff. & p. 159f.
Some symbols with their IPA equivalent are:
Literature
edit- Hans Bruchhausen und Heinz Feldhoff: Us Platt kalle un verstonn - Mundartwörterbuch Lützenkirchen-Quettingen. Bergisch Gladbach 2005. ISBN 3-87314-410-7
- Leo Lammert und Paul Schmidt: Neunkirchen-Seelscheider Sprachschatz, herausgegeben vom Heimat- und Geschichtsverein Neunkirchen-Seelscheid 2006. (ca. 7300 Wörter)
- Manfred Konrads: Wörter und Sachen im Wildenburger Ländchen, Rheinland-Verlag, Köln, 1981
- Maria Louise Denst: Olper Platt - Bergisches Mundart-Wörterbuch für Kürten-Olpe und Umgebung. Schriftenreihe des Bergischen Geschichtsvereins Abt. Rhein-Berg e. V. Band 29. Bergisch Gladbach 1999. ISBN 3-932326-29-6
- Theodor Branscheid (Hrsg): "Oberbergische Sprachproben. Mundartliches aus Eckenhagen und Nachbarschaft." Band 1, Eckenhagen, 1927.
- Heinrichs, Werner: Bergisch Platt - Versuch einer Bestandsaufnahme, Selbstverlag, Burscheid, 1978
- Georg Wenker: Das rheinische Platt. 1877.
- Georg Wenker: Das rheinische Platt, (Sammlung deutsche Dialektgeographie Heft 8), Marburg, 1915.
- Georg Cornelissen, Peter Honnen, Fritz Langensiepen (editor): Das rheinische Platt. Eine Bestandsaufnahme. Handbuch der rheinischen Mundarten Teil 1: Texte. Rheinland-Verlag, Köln. 1989. ISBN 3-7927-0689-X
- Helmut Fischer: 'Wörterbuch der unteren Sieg. Rheinische Mundarten. Beiträge zur Volkssprache aus den rheinischen Landschaften Band 4. Rheinland Verlag, Köln, 1985. ISBN 3-7927-0783-7
- Ludewig Rovenhagen: Wörterbuch der Aachener Mundart, Aachen, 1912.
- Prof. Dr. Will Herrmanns, Rudolf Lantin (editor): Aachener Sprachschatz. Wörterbuch der Aachener Mundart. Beiträge zur Kultur- und Wirtschaftsgeschichte Aachens und Seiner Umgebung, Band 1. Im Auftrag des Vereins „Öcher Platt“ für den Druck überarbeitet und herausgegeben von Dr. Rudolf Lantin. 2 Bände. Verlag J. A. Mayer, 1970. ISBN 3-87519-011-4
- Adolf Steins: Grammatik des Aachener Dialekts. Herausgegeben von Klaus-Peter Lange. Rheinisches Archiv Band 141. Böhlau-Verlag, Kölle, Weimar, Wien, 1998. ISBN 3-412-07698-8
- Dr. Karl Allgeier, Jutta Baumschulte, Meinolf Baumschulte, Richard Wolfgarten: Aachener Dialekt - Wortschatz, Öcher Platt - Hochdeutsch und Hochdeutsch - Öcher Platt. Öcher Platt e.V. Aachen, 2000.