The spinal accessory nucleus lies within the cervical spinal cord (C1-C5) in the posterolateral aspect of the anterior horn. The nucleus ambiguus is classically said to provide the "cranial component" of the accessory nerve. However, the very existence of this cranial component has been recently questioned and seen as contributing exclusively to the vagus nerve.
| Spinal accessory nucleus | |
|---|---|
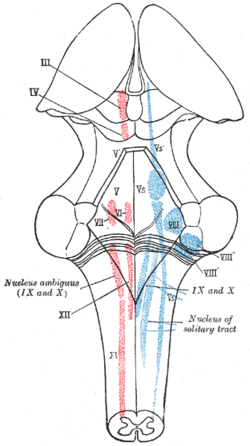 The cranial nerve nuclei schematically represented; dorsal view. Motor nuclei in red; sensory in blue. (Spinal accessory nucleus is at "XI".) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nucleus nervi accessorii, nucleus spinalis nervi accessorii |
| NeuroNames | 1708 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The terminology continues to be used in describing both human anatomy,[1] and that of other animals.[2]
Additional images
edit-
Nuclei of origin of cranial motor nerves schematically represented; lateral view.
-
Primary terminal nuclei of the afferent (sensory) cranial nerves schematically represented; lateral view.
References
edit- ^ Routal RV, Pal GP (2000). "Location of the spinal nucleus of the accessory nerve in the human spinal cord". J. Anat. 196 ( Pt 2) (2): 263–8. doi:10.1046/j.1469-7580.2000.19620263.x. PMC 1468059. PMID 10739022.
- ^ Ullah M, Mansor O, Ismail ZI, Kapitonova MY, Sirajudeen KN (2007). "Localization of the spinal nucleus of accessory nerve in rat: a horseradish peroxidase study". J. Anat. 210 (4): 428–38. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2007.00709.x. PMC 2100289. PMID 17428204.